The Tool Holder is the connector between the machine tool and the cutting tool. It's a crucial component affecting concentricity and dynamic balance, and should not be treated as an ordinary part. Concentricity determines the uniformity of cutting depth across the cutting edges during a single rotation of the tool; dynamic imbalance during spindle rotation will cause periodic vibrations.
Based on the taper of the machining center spindle tool mounting hole, tool holders are generally divided into two main categories:
1) SK general-purpose tool holders with a 7:24 taper
2) HSK vacuum tool holders with a 1:10 taper
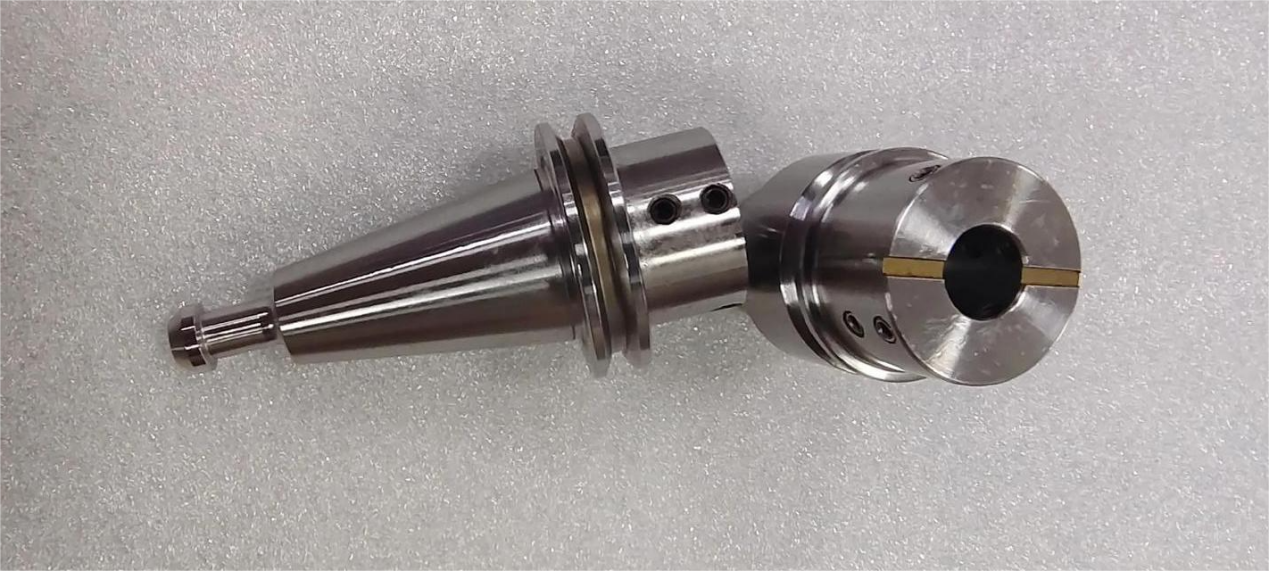

SK General-Purpose Tool Holders with a 7:24 Taper
7:24 refers to a 7:24 taper on the tool holder, providing individual taper positioning and a relatively long taper shank. The taper surface plays two important roles: precise positioning of the tool holder relative to the spindle and clamping the tool holder.

Advantages: Non-self-locking, allowing for quick tool loading and unloading; manufacturing the tool holder only requires machining the taper angle to a high precision to ensure connection accuracy, resulting in relatively low cost.
Disadvantages: During high-speed rotation, the tapered bore at the spindle tip expands. The amount of expansion increases with the rotation radius and speed, reducing the rigidity of the tapered connection. Under the pull of the tie rod, the axial displacement of the tool holder also changes. The radial dimension of the tool holder changes after each tool change, leading to unstable repeatability accuracy.
General-purpose tool holders with a 7:24 taper typically come in five standards and specifications:
1) International Standard ISO 7388/1 (IV or IT)
2) Japanese Standard MAS BT (BT)
3) German Standard DIN 2080 (NT or ST)
4) American Standard ANSI/ASME (CAT)
5) DIN 69871 (JT, DIN, DAT, or DV)
Tightening Method: NT type tool holders are tightened via a tie rod on conventional Machine Tools, also known as ST in China; the other four types are tightened via a pull stud at the tail of the tool holder on machining centers.
Versatility:
1) Currently, the most commonly used tool holders in China are the DIN 69871 type (i.e., JT) and the Japanese MAS BT type;
2) The DIN 69871 type tool holder can also be installed on machine tools with ANSI/ASME spindle taper bores;
3) The international standard ISO 7388/1 type tool holder can also be installed on machine tools with DIN 69871 and ANSI/ASME spindle taper bores. Therefore, in terms of versatility, the ISO 7388/1 type tool holder is the best.
HSK Vacuum Tool Holder with a Taper of 1:10
The HSK vacuum tool holder relies on the elastic deformation of the tool holder to ensure that not only does the 1:10 taper surface of the tool holder contact the 1:10 taper surface of the machine tool spindle bore, but the flange surface of the tool holder also makes close contact with the spindle surface. This double-sided contact system is superior to the 7:24 universal tool holder in terms of high-speed machining, connection rigidity, and overlap accuracy.
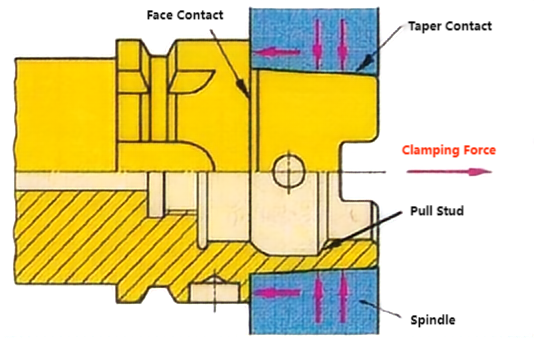
HSK vacuum toolholders enhance system rigidity and stability, improve product accuracy during high-speed machining, and shorten tool change times, playing a crucial role in high-speed machining. They are suitable for machine tool spindle speeds up to 60,000 rpm. HSK tool systems are widely used in aerospace, automotive, and precision mold manufacturing industries.
HSK toolholders are available in various types, including A, B, C, D, E, and F. Types A, E, and F are commonly used in machining centers (automatic tool changers).
The main differences between Type A and Type E are:
1) Type A toolholders have a drive groove, while Type E toolholders do not. Therefore, Type A toolholders transmit a relatively larger torque, making them suitable for heavier cuts. Type E toolholders transmit a smaller torque, limiting their application to lighter cuts.
2) In addition to the drive groove, Type A toolholders also have manual fixing holes and directional grooves, resulting in relatively poorer balance. Type E toolholders lack these features, making them more suitable for high-speed machining. The E and F types have identical mechanisms; the difference lies in the taper of the F type toolholder, which has the same name (e.g., E63 and F63). In other words, while both E63 and F63 have a flange diameter of φ63, the taper dimension of the F63 is identical to that of the E50. Therefore, compared to the E63, the F63 will have a higher rotational speed (due to a smaller spindle bearing).
Media Contact
Company Name: Qingdao Micro Precision Machinery Co., Ltd.
Email:Send Email
Phone: +86-15589891818
Address:No. 438, Wangsha Road, Chengyang District
City: Qingdao
Country: China
Website: https://www.mpmmachine.com/
