What is a Thermal Vacuum chamber (TVC)?A thermal vacuum chamber is a device primarily used to simulate ambient space conditions. The most common applications for TVCs involve satellite performance testing, thermal cycling control, and testing components, subsystems, and entire satellites in a fully controlled environment. These tests accurately replicate space conditions by simultaneously controlling two environmental parameters: pressure and temperature.The Importance of Satellite TestingVacuum conditions simulate the unique environment of ambient space where heat exchange can occur: through radiation and conduction. It is crucial to conduct pre-launch testing under all conditions that could potentially harm satellite performance. If a satellite's operating conditions in space are not checked beforehand, the most common risk is freezing or overheating of the satellite components themselves.It is also important to remember that satellites experience pressures below 10⁻⁶ millibars.Most component damage in space is caused by solar radiation not filtered by the atmosphere (AM0 – Air Mass 0). Depending on the orbital conditions the satellite must navigate, the heat exchange rate can be higher or lower. Some satellites orbit for 90 minutes, reaching temperatures of approximately 150°C in sunlight and -190°C during a solar eclipse.
The design is thermally analyzed using thermal models, then validated and tested. Huanyi has developed a series of thermal vacuum chambers (TVCs), leveraging its extensive experience in applying several technologies to environmental test simulations.
How does a thermal vacuum chamber work?
1. External Body
The external body of the test volume (container) is constructed from high-quality stainless steel. Its design is supported by FEM (finite element method) analysis to optimize the steel thickness while withstanding the pressure differential between the internal and external environments. Welding and surface finishes are optimized to minimize leaks and outgassing, making it possible to achieve deep vacuum conditions.
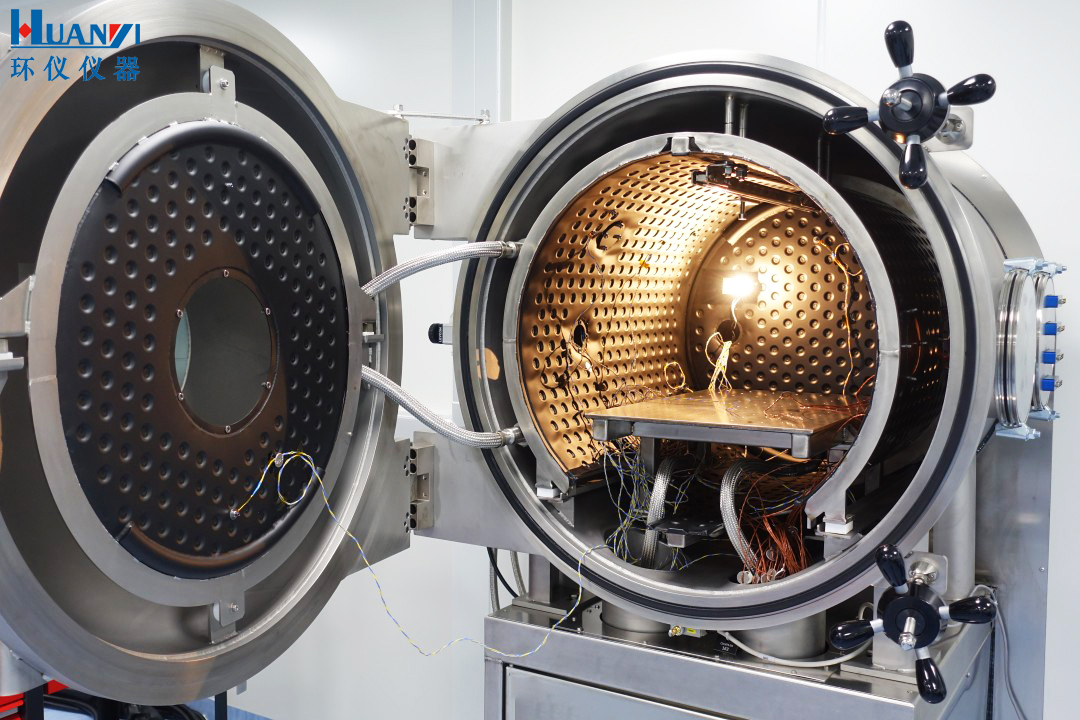
2. Thermal Field
The TVC's test volume is a thermally regulated stainless steel cylinder, called a shroud, that transfers heat to the device under test (DUT) through radiation from its inner surface. Two disc-shaped heat shields enclose the cylinder at each end to achieve a uniform temperature field around the device under test (DUT). The shield consists of two laminated sheets separated by a gap of several millimeters. This gap serves as a channel for the thermal fluid of the thermal power generation system. A specialized black paint is applied to this surface, resulting in a coating with high emissivity (>0.9) and low RML (recovered mass loss <1% at 150°C). Sometimes, a "hot plate" is placed within the test volume, on which samples are placed for thermal cycling via conduction heat transfer.
Depending on the application, different types of temperature control systems can be used:Temperature range -70°C to +150°C Mechanical cooling with an intermediate fluidA fluid (usually thermal oil) is circulated through a closed-circuit hood using a magnetically coupled pump, either cooled by refrigerated gas or electrically heated. One advantage of this system is its low cost.Temperature range -180°C to +150°C Pressurized gaseous nitrogenA dedicated blower circulates pressurized gaseous nitrogen through the hood, maintaining a density conducive to heat exchange and ensuring temperature uniformity across the entire radiant surface. Heating is provided by electric heaters, while cooling is achieved by spraying liquid nitrogen through the circuit. This system provides excellent temperature control over the entire temperature range.Temperature range -196°C to +150°C Liquid nitrogen + irradiatorIn this case, the hood is completely or partially filled with liquid nitrogen to a temperature of -90K (between -196°C and -185°C, depending on the pressure in the circuit). This creates a radiant cryogenic environment around the object being measured. Liquid nitrogen circulation in the housing can be either natural or forced by a pump. Heating elements (infrared lamps or emitters) placed in a special structure within the test volume are used to heat or moderately control the test object's temperature.
Temperature range: -196°C to +150°C. Liquid nitrogen + irradiator
In this case, the housing is completely or partially filled with liquid nitrogen, reaching a temperature of -90K (between -196°C and -185°C, depending on the pressure within the circuit). This creates a radiant cryogenic environment around the test object. Liquid nitrogen circulation in the housing can be either natural or forced by a pump. Heating elements (infrared lamps or emitters) placed in a special structure within the test volume are used to heat or moderately control the test object's temperature.
Media Contact
Company Name: Dongguan Huanyi Instruments Technology Co., Ltd.
Email:Send Email
Country: China
Website: https://www.huanyitestchamber.com/